Fixed Window Algorithm
How it works
- Divides the timeline into fixed-size time windows, each with its own counter.
- Each incoming request increments the counter.
- If the counter reaches the predefined threshold, additional requests are dropped until the next window.
Problem with Fixed Window Algorithm:
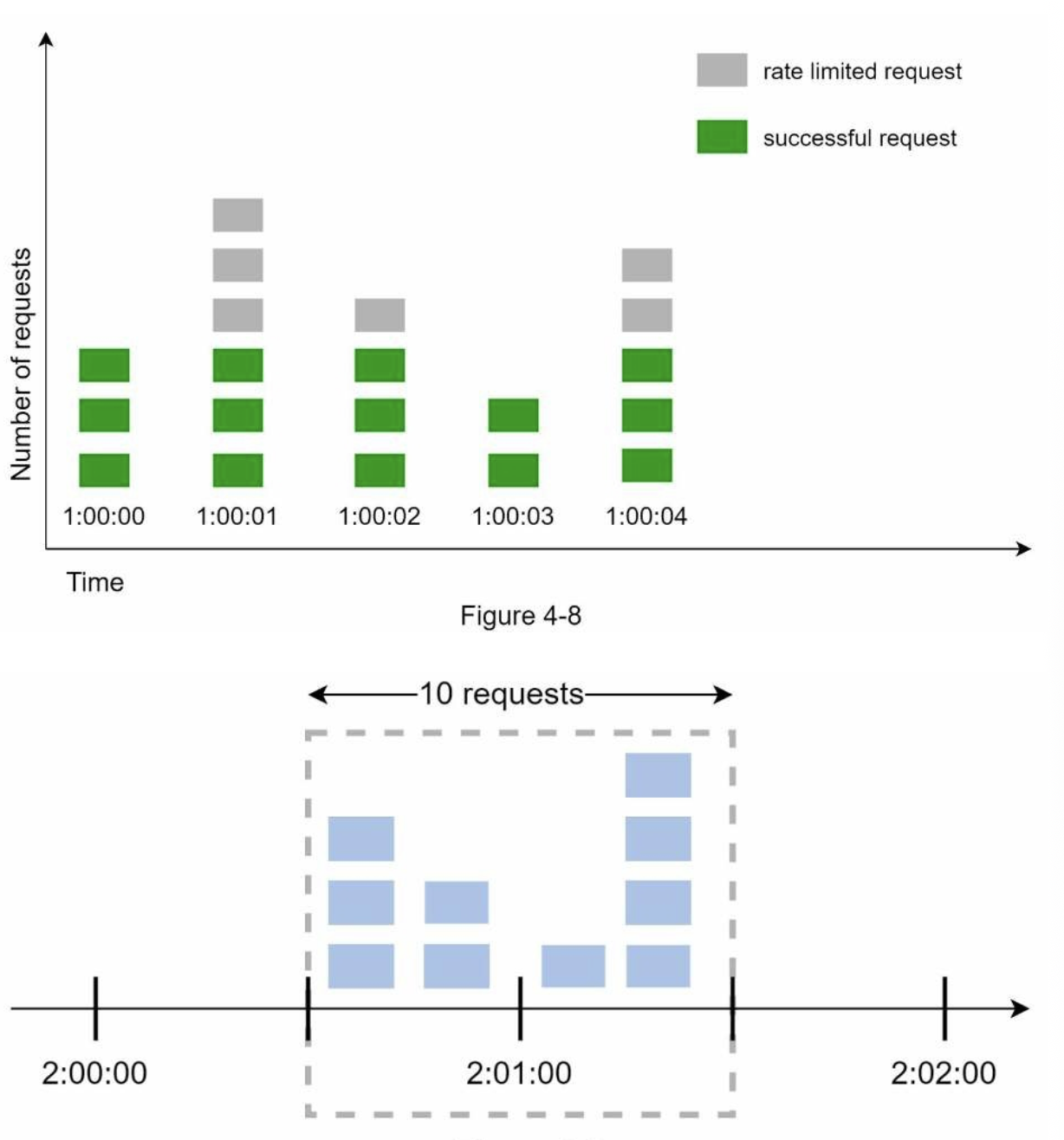
- Traffic bursts at window edges: A burst of traffic at the beginning or end of a window can cause more requests than allowed.
Example (1-minute window with 5 requests limit):
5 requests are allowed between 2:00:00 and 2:01:00, and another 5 between 2:01:00 and 2:02:00. Between 2:00:30 and 2:01:30, 10 requests pass through (double the allowed limit), as both time windows overlap.
Sample Implementaion
import time
class FixedWindowRateLimiter:
def __init__(self, limit, window_size):
"""
Initialize the rate limiter.
:param limit: Maximum number of requests allowed in each window.
:param window_size: The size of the window in seconds.
"""
self.limit = limit
self.window_size = window_size
self.request_count = 0
self.window_start_time = time.time()
def is_rate_limited(self):
"""
Check if the request is allowed or if it exceeds the limit for the current window.
:return: True if rate limit exceeded, False if request is allowed.
"""
current_time = time.time()
# If current window has passed, reset the counter
if current_time - self.window_start_time >= self.window_size:
self.window_start_time = current_time
self.request_count = 0
# Increment the request count
self.request_count += 1
# If the request count exceeds the limit, rate limit is triggered
if self.request_count > self.limit:
return True # Rate limit exceeded
return False # Request is allowed
# Example usage
rate_limiter = FixedWindowRateLimiter(limit=3, window_size=1) # 3 requests per 1 second window
# Simulating requests
for i in range(5):
if rate_limiter.is_rate_limited():
print(f"Request {i+1} is rate-limited.")
else:
print(f"Request {i+1} is allowed.")
time.sleep(0.2) # Wait 200 ms between requests